Setting up a Kubernetes cluster using Docker in Docker | Callista
Setting up a Kubernetes cluster using Docker in Docker | Callista
Setting up a Kubernetes cluster using Docker in Docker | Callista


|
Blogg
Här finns tekniska artiklar, presentationer och nyheter om arkitektur och systemutveckling. Håll dig uppdaterad, följ oss på Twitter

In this blog post I will describe how to set up a local Kubernetes cluster for test purposes with a minimal memory usage and fast startup times, using Docker in Docker instead of traditional local virtual machines.
This blog post is part of the blog series - Trying out new features in Docker.
Background
For a background on how Docker in Docker can help us to set up a local Kubernetes cluster, see the Background section in the blog post Setting up a Docker Swarm cluster using Docker in Docker.
This blog post is not an introduction to Kubernetes and the components that builds up a Kubernetes cluster. For an introduction of the concepts used in Kubernetes see: kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/.
We are going to use the GitHub project Mirantis/kubeadm-dind-cluster to set up a Kubernetes cluster using Docker in Docker and we will use Docker for Mac to act as the Docker Host for the Kubernetes nodes (running as containers in Docker for Mac).
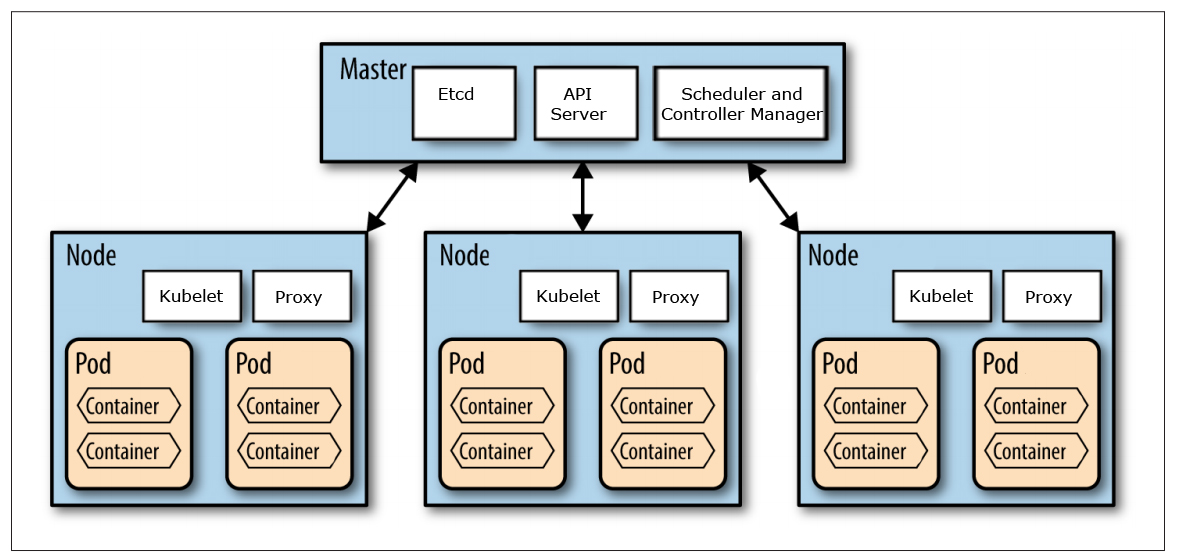
Source: http://nishadikirielle.blogspot.se/2016/02/kubernetes-at-first-glance.html
Installation
First, you need to have Docker for Mac installed, I’m on version 17.09.1-ce-mac42.
Next, you also need to have jq and md5sha1sum installed to be able to follow my instructions below. If you use Homebrew, they can be installed with:
brew install jq
brew install md5sha1sum
Finally, clone the Git repo Mirantis/kubeadm-dind-cluster from GitHub and jump into the fixed folder:
git clone https://github.com/Mirantis/kubeadm-dind-cluster.git
cd kubeadm-dind-cluster/fixed
We are good to go!
Setup
Start up a Kubernetes v1.8 cluster requesting 3 worker nodes in the cluster (default is 2):
NUM_NODES=3 ./dind-cluster-v1.8.sh up
The first time the up command is executed it will take a few minutes and produce lot of output in the terminal window…
…in the end it should say something like:
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
kube-master Ready master 2m v1.8.4
kube-node-1 Ready <none> 1m v1.8.4
kube-node-2 Ready <none> 1m v1.8.4
kube-node-3 Ready <none> 47s v1.8.4
* Access dashboard at: http://localhost:8080/ui
Note: If you start up the cluster again later on, it will only take a minute.
Verify that you can see the master and worker nodes as ordinary containers in Docker for Mac:
docker ps
It should report something like:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
766582a93d1f mirantis/kubeadm-dind-cluster:v1.8 "/sbin/dind_init s..." 9 hours ago Up 9 hours 8080/tcp kube-node-3
e1fc6bec1f23 mirantis/kubeadm-dind-cluster:v1.8 "/sbin/dind_init s..." 9 hours ago Up 9 hours 8080/tcp kube-node-2
b39509b9db77 mirantis/kubeadm-dind-cluster:v1.8 "/sbin/dind_init s..." 9 hours ago Up 9 hours 8080/tcp kube-node-1
a01be2512423 mirantis/kubeadm-dind-cluster:v1.8 "/sbin/dind_init s..." 9 hours ago Up 9 hours 127.0.0.1:8080->8080/tcp kube-master
View
Ok, so let’s see if we actually have a Kubernetes cluster up and running:
kubectl get nodes
It should result in a response like:
NAME STATUS AGE VERSION
kube-master Ready 2m v1.8.4
kube-node-1 Ready 55s v1.8.4
kube-node-2 Ready 1m v1.8.4
kube-node-3 Ready 1m v1.8.4
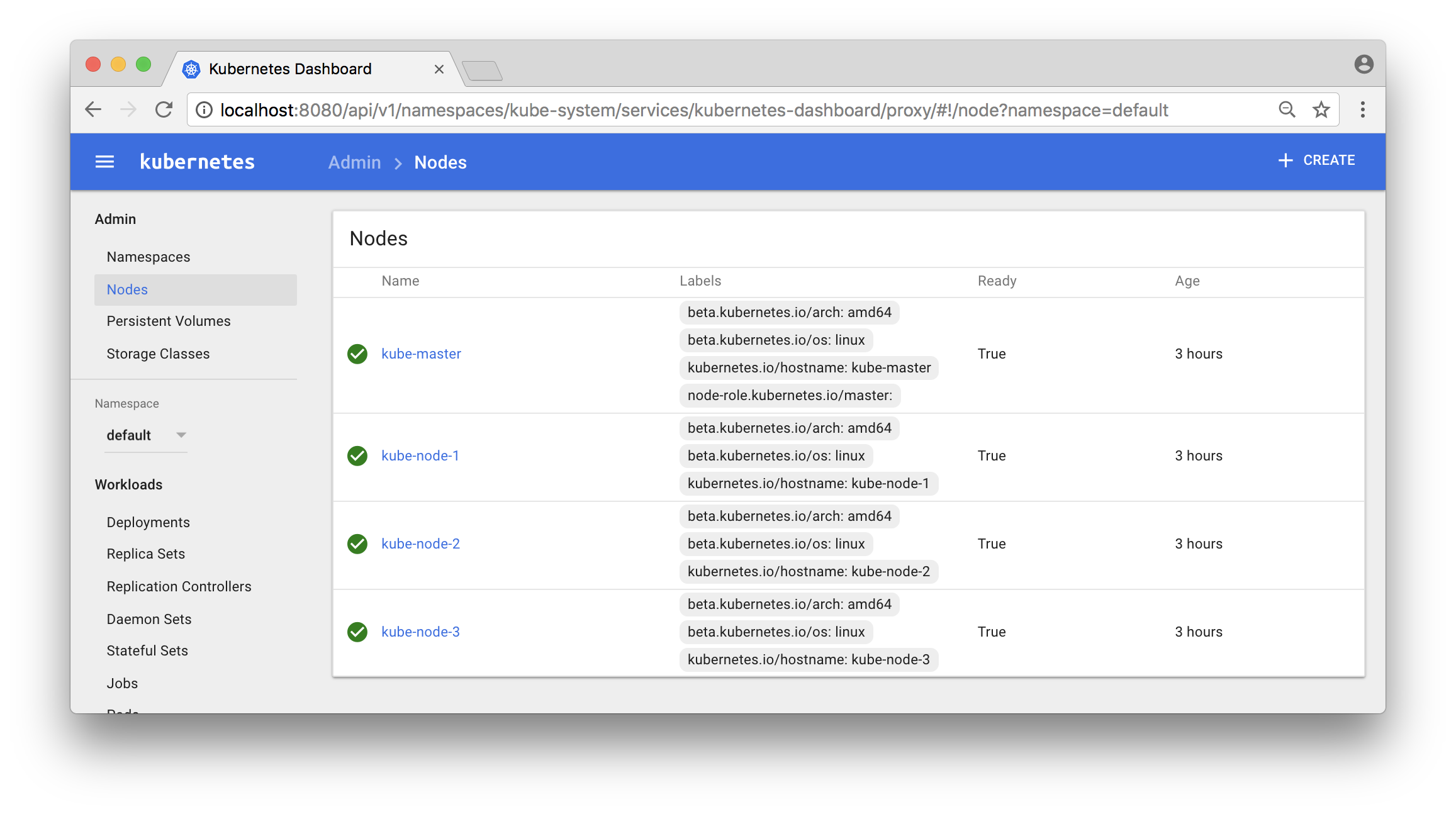
Also try out Kubernetes Dashboard at: localhost:8080/ui
Click on the “Nodes” - link in the menu to the left and you should see something like:
Deploy
Now, let’s deploy a service and try it out!
I have a very simple Docker image magnuslarsson/quotes:go-22 (written in Go) that creates some random quotes about successful programming languages.
We will create a Deployment of this Docker Image and a Service that expose it on each node in the Kubernetes cluster using a dedicated port (31000). The creation of the Deployment object will automatically also create a Replica Set and a Pod.
Note: In more production like environment we should also set up an external load balancer, like HAProxy or NGINX in front of the Kubernetes cluster to be able to expose one single entry point to all services in the cluster. But that is out of scope for this blog post and left as an exercise for the interested reader :-)
First, switch to the default namespace:
kubectl config set-context $(kubectl config current-context) --namespace=default
The default namespace should only contain one pre-created object, run the command:
kubectl get all
It should report:
NAME CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
svc/kubernetes 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 5h
Create a file named quotes.yml with the following command:
cat <<EOF > quotes.yml
apiVersion: apps/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: quotes
labels:
app: quotes-app
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: quotes-app
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: quotes-app
spec:
containers:
- name: quotes
image: magnuslarsson/quotes:go-22
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: quotes-service
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: quotes-app
ports:
- port: 8080
targetPort: 8080
nodePort: 31000
EOF
Create the Deployment and Service objects with the following command:
kubectl create -f quotes.yml
Verify that we got the expected objects created, using the following command:
kubectl get all
Expect output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
po/quotes-77776b5bbc-5lll7 1/1 Running 0 45s
NAME CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
svc/kubernetes 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 5h
svc/quotes-service 10.105.185.117 <nodes> 8080:31000/TCP 45s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deploy/quotes 1 1 1 1 45s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
rs/quotes-77776b5bbc 1 1 1 45s
Note: In the output above short names are used for object types:
po: Podsvc: Servicedeploy: Deploymentrs: Replica Set
We can now try it out using curl from one of the worker nodes:
docker exec kube-node-2 curl localhost:31000/api/quote -s -w "\n" | jq
Output should look like:
{
"ipAddress": "quotes-77776b5bbc-5lll7/10.192.3.4",
"quote": "In Go, the code does exactly what it says on the page.",
"language": "EN"
}
The most interesting part of the response from the service is actually the field ipAddress, that contains the hostname and ip address of the pod that served the request, quotes-77776b5bbc-5lll7/10.192.3.4 in the sample response above.
Scale
This can be used to verify that scaling of a service actually works. In the output from a scaled service we expect different values in the ipAddress - field from subsequent requests, indicating that the request is load balanced over the available pods.
Let’s try it out, shall we?
First, start a loop that use curl to sends one request per second to the quote-service and prints out the ipAddress - field from the response:
while true; do docker exec kube-node-2 curl localhost:31000/api/quote -s -w "\n" | jq -r .ipAddress; sleep 1; done
Initially the output should return one and the same hostname and IP address, since we only have one pod running in the service:
quotes-77776b5bbc-5lll7/10.192.3.4
quotes-77776b5bbc-5lll7/10.192.3.4
quotes-77776b5bbc-5lll7/10.192.3.4
quotes-77776b5bbc-5lll7/10.192.3.4
Now, scale the quote-service by adding 8 new pods to it (9 in total):
kubectl scale --replicas=9 deployment/quotes
Verify that you can see all 9 quote-service pods and also to what node they are deployed:
kubectl get pods -o wide
Expected output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE
quotes-77776b5bbc-42wgk 1/1 Running 0 1m 10.192.4.9 kube-node-3
quotes-77776b5bbc-c8mkf 1/1 Running 0 1m 10.192.3.8 kube-node-2
quotes-77776b5bbc-dnpm8 1/1 Running 0 25m 10.192.3.4 kube-node-2
quotes-77776b5bbc-gpk85 1/1 Running 0 1m 10.192.2.8 kube-node-1
quotes-77776b5bbc-qmspm 1/1 Running 0 1m 10.192.4.11 kube-node-3
quotes-77776b5bbc-qr27h 1/1 Running 0 1m 10.192.3.9 kube-node-2
quotes-77776b5bbc-txpcq 1/1 Running 0 1m 10.192.2.9 kube-node-1
quotes-77776b5bbc-wb2qt 1/1 Running 0 1m 10.192.4.10 kube-node-3
quotes-77776b5bbc-wzhzz 1/1 Running 0 1m 10.192.2.7 kube-node-1
Note: We got three pods per node, as expected!
You can also use the Dashboard to see what pods that run in a specific node:
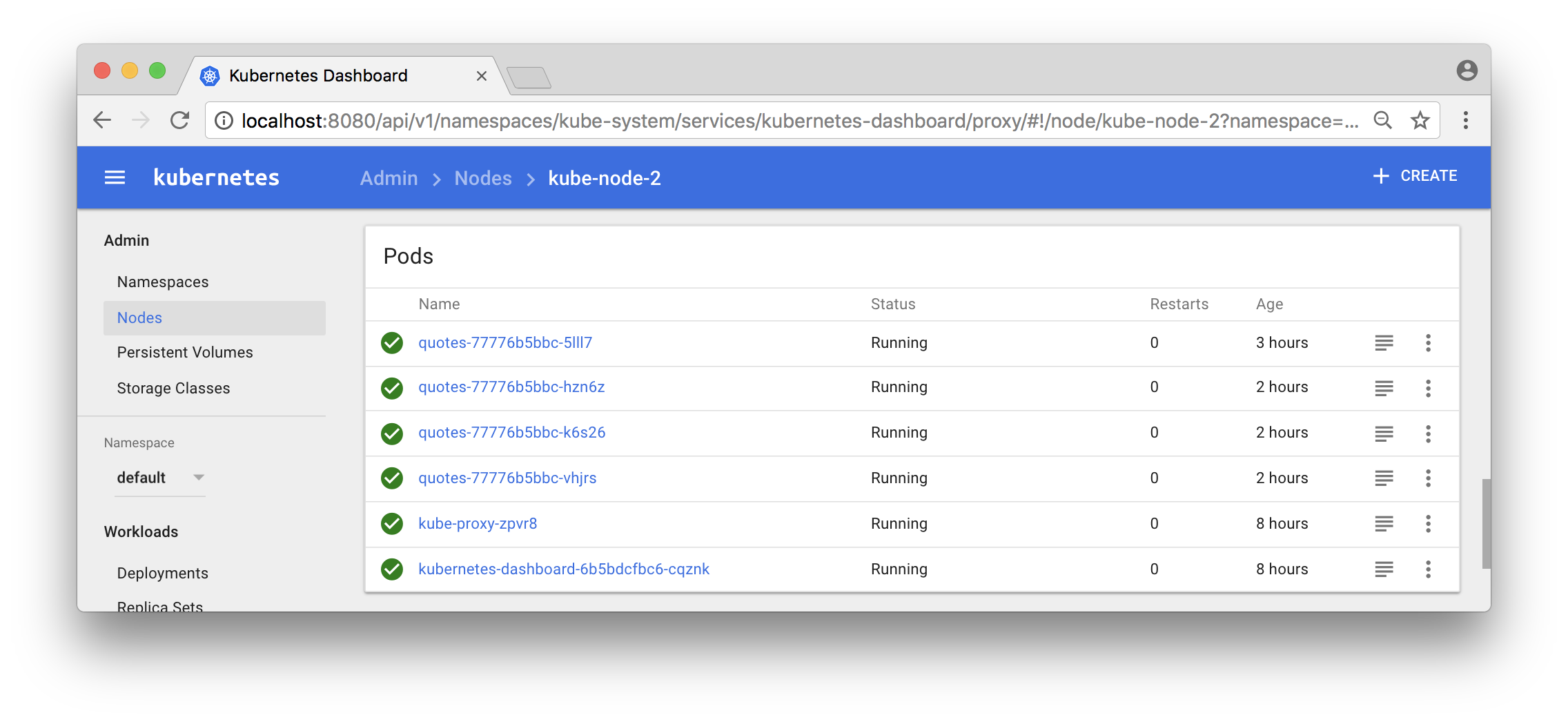
Now, the output from the curl - loop should report different hostnames and ip addresses as the requests are load balanced over the 9 pods:
quotes-77776b5bbc-gpk85/10.192.2.8
quotes-77776b5bbc-42wgk/10.192.4.9
quotes-77776b5bbc-txpcq/10.192.2.9
quotes-77776b5bbc-txpcq/10.192.2.9
quotes-77776b5bbc-wb2qt/10.192.4.10
quotes-77776b5bbc-txpcq/10.192.2.9
Great, isn’t it?
Resilience
Now, let’s expose the container orchestrator, i.e. Kubernetes, to some problems and see if it handles them as expected!
Kill some pods
First, let’s shut down some arbitrary pods and see if the orchestrator detects it and start new ones!
Note: We will actually kill the container that runs within the pod, not the pod itself.
Start a long running command, using the --watch flag, that continuously reports changes in the state of the Deployment object:
kubectl get deployment quotes --watch
Initially, it should report:
NAME DESIRED CURRENT UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
quotes 9 9 9 9 1d
Note: The command hangs, waiting for state changes to be reported
To keep things relatively simple, let’s kill all quote-services running on the first worker node:
CIDS=$(docker exec kube-node-1 docker ps --filter name=k8s_quotes_quotes -q)
docker exec kube-node-1 docker rm -f $CIDS
The command should respond with the ids of the killed containers:
e780545ddd17
ddd260ba3f73
b4e07e736028
Now, go back to the “_deployment watch_” - command and see what output it produces!
It should be something like:
quotes 9 9 9 8 1d
quotes 9 9 9 7 1d
quotes 9 9 9 6 1d
quotes 9 9 9 7 1d
quotes 9 9 9 8 1d
quotes 9 9 9 9 1d
The output shows how Kubernetes detected that it got short of available pods and compensated that by scheduling new containers for the affected pods.
Worker node off line
Now, let’s make it even worse by removing a worker node, simulating that it is taken off line for maintenance work. Let’s mark kube-node-3 as no longer accepting either existing pods or scheduling of new pods:
kubectl drain kube-node-3 --ignore-daemonsets
The command reports back what pods that was evicted from the node:
pod "quotes-77776b5bbc-jlwtb" evicted
pod "quotes-77776b5bbc-7d6gc" evicted
pod "quotes-77776b5bbc-cz8sp" evicted
Kubernetes will however automatically detect this and start new ones on the remaining nodes:
kubectl get pods -o wide
Reports back:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE
quotes-77776b5bbc-28r7w 1/1 Running 0 11s 10.192.2.10 kube-node-1
quotes-77776b5bbc-7hxd5 1/1 Running 0 11s 10.192.3.10 kube-node-2
quotes-77776b5bbc-c8mkf 1/1 Running 0 7m 10.192.3.8 kube-node-2
quotes-77776b5bbc-dnpm8 1/1 Running 0 31m 10.192.3.4 kube-node-2
quotes-77776b5bbc-gpk85 1/1 Running 0 7m 10.192.2.8 kube-node-1
quotes-77776b5bbc-grcqn 1/1 Running 0 11s 10.192.2.11 kube-node-1
quotes-77776b5bbc-qr27h 1/1 Running 0 7m 10.192.3.9 kube-node-2
quotes-77776b5bbc-txpcq 1/1 Running 0 7m 10.192.2.9 kube-node-1
quotes-77776b5bbc-wzhzz 1/1 Running 0 7m 10.192.2.7 kube-node-1
Note: The three pods with an age of 11 sec are the new ones.
We can also see that the node is reported to being unavailable for scheduling of pods:
kubectl get node
Reports:
NAME STATUS AGE VERSION
kube-master Ready 1d v1.8.4
kube-node-1 Ready 1d v1.8.4
kube-node-2 Ready 1d v1.8.4
kube-node-3 Ready,SchedulingDisabled 1d v1.8.4
Great!
Let’s wrap up by making the node available again:
kubectl uncordon kube-node-3
The node is now reported to be back on line:
kubectl get node
Results in:
NAME STATUS AGE VERSION
kube-master Ready 1d v1.8.4
kube-node-1 Ready 1d v1.8.4
kube-node-2 Ready 1d v1.8.4
kube-node-3 Ready 1d v1.8.4
But none of the existing pods are automatically rescheduled to the node:
kubectl get pods -o wide
Still reports that all pods runs on node 1 and 2:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE
quotes-77776b5bbc-28r7w 1/1 Running 0 4m 10.192.2.10 kube-node-1
quotes-77776b5bbc-7hxd5 1/1 Running 0 4m 10.192.3.10 kube-node-2
quotes-77776b5bbc-c8mkf 1/1 Running 0 11m 10.192.3.8 kube-node-2
quotes-77776b5bbc-dnpm8 1/1 Running 0 36m 10.192.3.4 kube-node-2
quotes-77776b5bbc-gpk85 1/1 Running 0 11m 10.192.2.8 kube-node-1
quotes-77776b5bbc-grcqn 1/1 Running 0 4m 10.192.2.11 kube-node-1
quotes-77776b5bbc-qr27h 1/1 Running 0 11m 10.192.3.9 kube-node-2
quotes-77776b5bbc-txpcq 1/1 Running 0 11m 10.192.2.9 kube-node-1
quotes-77776b5bbc-wzhzz 1/1 Running 0 11m 10.192.2.7 kube-node-1
We can, however, manually rebalance our pods with the commands:
kubectl scale --replicas=6 deployment/quotes
kubectl scale --replicas=9 deployment/quotes
Verify:
kubectl get pods -o wide
Reports the expected three pod per node again:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE
quotes-77776b5bbc-2q26w 1/1 Running 0 1s 10.192.4.13 kube-node-3
quotes-77776b5bbc-bbhcb 1/1 Running 0 1s 10.192.4.14 kube-node-3
quotes-77776b5bbc-c8mkf 1/1 Running 0 13m 10.192.3.8 kube-node-2
quotes-77776b5bbc-dnpm8 1/1 Running 0 37m 10.192.3.4 kube-node-2
quotes-77776b5bbc-gpk85 1/1 Running 0 13m 10.192.2.8 kube-node-1
quotes-77776b5bbc-qr27h 1/1 Running 0 13m 10.192.3.9 kube-node-2
quotes-77776b5bbc-trrdh 1/1 Running 0 1s 10.192.4.12 kube-node-3
quotes-77776b5bbc-txpcq 1/1 Running 0 13m 10.192.2.9 kube-node-1
quotes-77776b5bbc-wzhzz 1/1 Running 0 13m 10.192.2.7 kube-node-1
Teardown
That’s it, let’s remove the Kubernetes cluster:
./dind-cluster-v1.8.sh down
If you start up the cluster again with the up command, it will start up much faster than the first time!
If you don’t want to start up the cluster again, at least in any near time, you can also clean up some data created for the cluster:
./dind-cluster-v1.8.sh clean
If you start up the cluster again after a clean command you are back to the very long startup time.
Next up…
For more blog posts on new features in Docker, see the blog series - Trying out new features in Docker.
Tack för att du läser Callistas blogg.
Hjälp oss att nå ut med information genom att dela nyheter och artiklar i ditt nätverk.
Kommentarer
Stockholm
Drottninggatan 55
111 21 Stockholm
Tel: +46 8 21 21 42
Göteborg
Fabriksgatan 13
412 50 Göteborg
Tel: +46 31 20 19 18
Följ oss
© 2022 Callista Enterprise AB